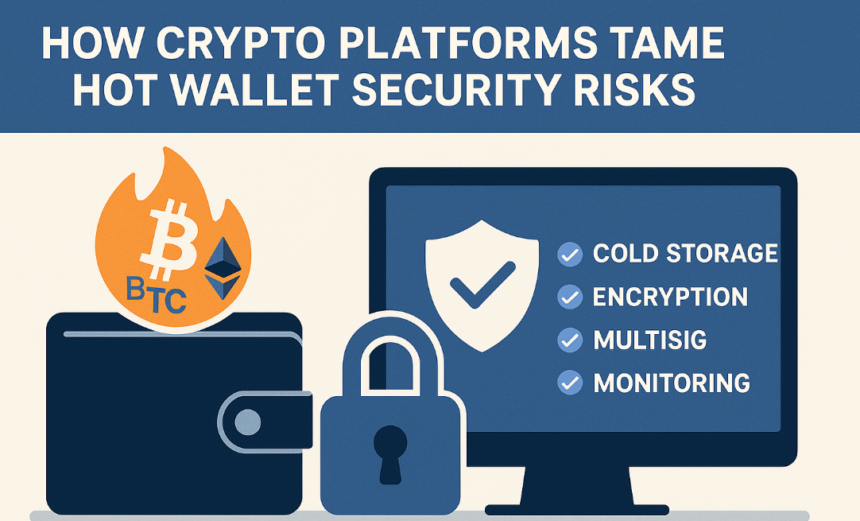
I’ll go over how cryptocurrency platforms manage hot wallet security threats in this post. Hot wallets are necessary for quick transactions and trade, but they are vulnerable to insider threats, phishing, and hacking.
- What is Hot Wallet?
- How Crypto Platforms Tame Hot Wallet Security Risks
- Example: Securing Hot Wallets at a Crypto Exchange
- Step 1: Multi-Signature Wallet (Multi-Sig)
- Step 2: Integration of Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
- Step 3: Implementing of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Step 5: Whitelisting and Limitations on Transactions
- Step 6: consistent Penetration Testing and Security Audits
- Step 7: Insurance and Incident Response
- Key Security Risks of Hot Wallets
- Hacking and Cyberattacks
- Phishing and Social Engineering
- Malware and Ransomware
- Insider Threats
- Software Vulnerabilities
- Transaction Errors and Mismanagement
- Core Security Measures Used by Platforms
- Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) Wallets
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Transaction Limits and Whitelisting
- Real-Time Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
- Secure Communication and Encryption
- Incident Response Planning
- Compliance and Governance Frameworks
- Regulatory Compliance
- Internal Security Policies
- Regular Audits and Reporting
- Third Party Penetration Testing
- Employee Training and Awareness Programs
- Governance Committees
- Policies for Reporting and Documenting Incidents
- Adherence to Global Standards of Security
- Balancing Security with User Experience
- Speed of Withdrawals vs. Withdrawals Security Checks
- No Friction User Authentication
- Helpful Security Alerts
- User Selectable Security
- Guidance and Education
- Security Tools Integration
- Feedback Integration
- Focus on Mobile and Cross-Platform
- Future Trends in Hot Wallet Security
- Advantage & Disadvantage
- Conclusion
- FAQ
To safeguard money while guaranteeing a seamless user experience and dependable access to digital assets, cryptocurrency platforms combine technical safeguards, real-time monitoring, and robust governance.
What is Hot Wallet?
Hot wallets are digital wallets used for storing cryptocurrency assets on the internet. This type of wallet allows users to sending and receive cryptographic assets. This is opposed to cold wallets which are offline.
Cold wallets are offline and are used for long-term storage. Since hot wallets are easily accessible, they are used for daily transactions, trades and liquidity management on exchanges. Because hot wallets are used for transactions and trading, they can be used are web wallets, mobile applications, or even desktop software.
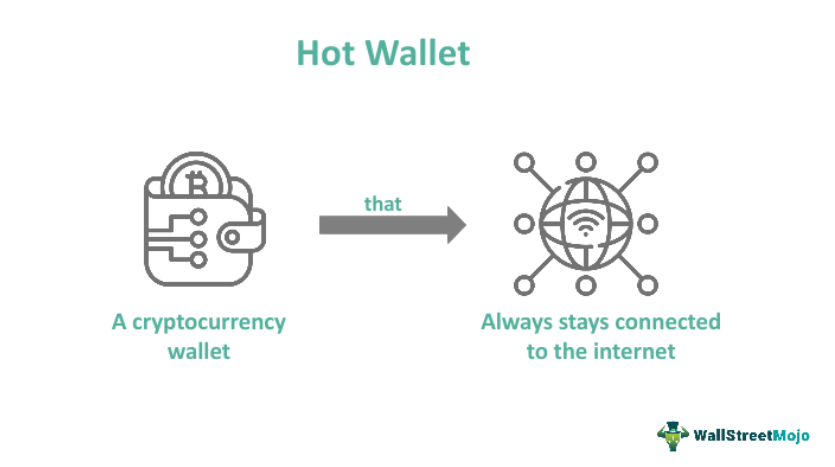
Since hot wallets store private keys online, it enables instant access for transaction, but exposes the assets to online threats from outside the wallet, including cyber threats and hacking. Because they are always online, they are use vulnerable to hacks, phishing, malware, and attacks from insiders.
This is why online crypto trading platforms use security features like authorisation from multiple signatures, transaction limits, real-time monitoring, and security modules. Regardless of the associated risks, hot wallets are vital for crypto trading and platforms and security of the hot wallets is why responsible trading platforms exist.
How Crypto Platforms Tame Hot Wallet Security Risks
Example: Securing Hot Wallets at a Crypto Exchange
Step 1: Multi-Signature Wallet (Multi-Sig)
- Hot wallets have a private key that requires multiple signatories to approve a transaction.
- For example, one key might require 3 out of 5 executives to approve a movement of funds.
- This avoids the potential exploitation of a compromised key.
Step 2: Integration of Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
- The private keys are kept within HSMs, or Hardware Security Modules, which are secure-by-design devices.
- HSMs encrypt the keys and complete secure transaction processing without exposing the keys to the internet.
Step 3: Implementing of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Employees are given access rights according to their assigned roles.
- Only security engineers can initiate transfers, while the rest can only view the balances.
- This minimizes the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access.
Step 4: Monitoring and Alerts in Real Time
- Artificial intelligence and automated systems are used to monitor any suspicious activity.
- The system alerts in the event of unusual withdrawals, a series of failed logins, or any transactions that occur outside of normal business hours.
Step 5: Whitelisting and Limitations on Transactions
- To help mitigate possible losses, there is a limit to how much can be withdrawn each day.
- To prevent the possibility of sending money to a hacker’s wallet, money can only be sent to whitelisted addresses that have been approved beforehand.
Step 6: consistent Penetration Testing and Security Audits
- Security specialists from outside of the company examine the hot wallet system to look for weaknesses.
- Audits are used to assess if a company is following the proper security protocols and to find any potential problems.
Step 7: Insurance and Incident Response
- The exchange has a breach response plan that includes how they will notify users and if funds will be recoverable.
- Some exchanges have insurance for a portion of the assets that are held in the hot wallet to protect against theft.
Key Security Risks of Hot Wallets
Hacking and Cyberattacks
- Because hot wallets are always online, they can become a target for hackers.
- Attacks can occur through brute force, credential stuffing, and some may try to take advantage of weak exchanges.
Phishing and Social Engineering
- Employees may also be socially engineered to reveal their private keys to a hacker or revealing their login credentials.
- To obtain access, a hacker can target a users fake websites, spoof emails, or malicious apps.
Malware and Ransomware
- Capturing the keystrokes of the user or wallets can be done through devices or malware that accesses the wallets.
- Access can be locked in a ransomware attack, or sensitive information can be leaked from the wallet.
Insider Threats
- Employees or contractors with access to the wallets or hot wallet may take advantage of the funds.
- Theft internally becomes a larger threat with a lack of role-based structure.
Software Vulnerabilities
- Software that has bugs or a poorly coded application can be forcibly updated.
- Wallet software, APIs, and smart contracts that are coded poorly or outdated are often less likely to be called secure.
Transaction Errors and Mismanagement
- Irrecoverably losing the funds can occur through: an address that is mistyped, a target account that is wrong or a wallet that is incorrect.
Core Security Measures Used by Platforms
Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) Wallets
- Any transaction must get approved by multiple signers.
- One broken key is never enough to steal any money.
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
- Special devices who’s integrated circuits are designed to be protected from tampering. They safely sign transactions online while storing their private key offline.
- Keys remain unexposed and protected from different hacks or malware attacks.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Wallets are a protected under the diverging roles and responsibilities of the employees.
- No unprivileged employees can start or sign a transaction.
Transaction Limits and Whitelisting
- Putting a daily limit on withdrawals minimizes the impact of any compromises.
- Whitelisting makes it so money can only get send to wallets on the whitelist.
Real-Time Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Wallets are monitored constantly and tracked for any irregular activities.
- Usage of machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and notified users in order to pinpoint unauthorized access or fraud.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
- Wallet infra are audited both internally and externally to see if there are any flaws within the system.
- Pen testing makes sure the system is secure by simulating possible real attacks on the system.
Secure Communication and Encryption
- Data storage and communications between wallets are systematically secured and encrypted.
- Ensures that sensitive data is not accessible to attackers.
Incident Response Planning
- Steps to breach detection, containment, and recovery of funds are outlined.
- In the event of a security incident, this allows for immediate action to be taken to limit the extent of the damage.
Compliance and Governance Frameworks
Regulatory Compliance
- Meeting requirements of the crypto industry and its regulations including Anti-Money Laundering and Know Your Customer requirements.
- This compliance allows for the legal operation of the business, as well as fosters trust among customers and financial stakeholders.
Internal Security Policies
- Platforms establish policies that outline the access of wallets, the approvals of transactions and the tasks of each employee.
- Policies establish a strong culture and eliminate the risk of the human factor, either by negligence or by actions from a malicious actor from within.
Regular Audits and Reporting
- Internal and external audits take place on a recurring basis that analyze the operational practices and security of the wallets.
- Stakeholders gain a level of transparency, and there is a means to ensure that compliance is not static.
Third Party Penetration Testing
- Some firms that operate hot wallets are evaluated by external security companies as to where their weaknesses are.
- This means that vulnerable places are aware of potential attackers, before attackers gain access to those places.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
- Breaches that are caused by negligence are kept to a minimum by training staff on phishing, social engineering, and security policies.
- The employee’s adherence to the policies is far more tolerant of negligence.
Governance Committees
- There are calls for separate committees to deal with risk oversight, security policy, and the enforcement of all policies.
- This approach is more comprehensive with regard to the management of all decisions that are critical to the business.
Policies for Reporting and Documenting Incidents
- Systems provide documentation for all activities, including transactions, instances of access, and security activities.
- Assists in tracking security incidents, fulfilling regulatory requirements, and enhancing protective measures.
Adherence to Global Standards of Security
- Compliance with ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, or other applicable cybersecurity frameworks.
- Users and regulators see this as a positive sign of commitment to security and risk management.
Balancing Security with User Experience
Speed of Withdrawals vs. Withdrawals Security Checks
- User experience will suffer if platforms impose strict withdrawal speed limits.
- Verifying withdrawals with MFA (multi-factor authentication) or a multi-sig approvals introduce trade-offs between speed and safety.
No Friction User Authentication
- User Authentication methods that can eliminate friction include biometrics, some secure password managers, and single sign-on (SSO) solutions.
- Users need to be able to securely access their wallets without unnecessary complications.
Helpful Security Alerts
- Alerts for pending or completed transactions that show unusual account activity need to be helpful and to the point in order to avoid unnecessary confusion.
- Users need to respond to alerts without panic or mistake.
User Selectable Security
- Users should be able to select their preferred level of security, e.g. more security with bigger account balances and less security with smaller transactions.
- Users are able to choose between convenience and security.
Guidance and Education
- Avoiding security and usability trade-offs requires users to make less educated mistakes. Provide more secure wallet usage tutorials, phishing, withdrawal guides, and more.
Security Tools Integration
- Security should be integrated with and behind the scenes of seamless normal transactions.
- E.g. flagged transactions or monitoring, AI based suspicious activity, and automatic fraud detection.
Feedback Integration
- Identify pain points with focus group user feedback on security processes.
- Improve safety and usability with policy and interface adjustments.
Focus on Mobile and Cross-Platform
- Security features are the same on mobile, web, and desktop.
- Users won’t face security gaps or confusion on different devices.
Future Trends in Hot Wallet Security

Hot wallet security is evolving toward more sophisticated, automated, and decentralized safeguards that strike a balance between risk reduction and accessibility. By reducing reliance on a single private key, innovations like threshold signature methods and Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets make hacking much more challenging.
Zero-trust architectures are being used, in which all access requests—including those from internal employees—are constantly validated. While on-chain analytics allow for predicted risk assessments, platforms are increasingly using AI-powered anomaly detection to spot questionable transactions in real time.
Exchanges are also being forced by industry standards and regulatory pressure to maintain open security audits and execute thorough insurance coverage. In order to make hot wallets safer without sacrificing speed or user convenience, the general tendency is to combine state-of-the-art technology, proactive monitoring, and governance structures.
Advantage & Disadvantage
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Fast and Convenient Access – Ideal for daily transactions and trading. | High Cybersecurity Risk – Always online, making them vulnerable to hacking and phishing. |
| Supports Real-Time Trading – Enables instant withdrawals and deposits for users. | Insider Threats – Employees with access can misuse funds if proper controls are not in place. |
| Easy Integration – Works with exchanges, apps, and DeFi platforms seamlessly. | Limited Long-Term Storage – Not suitable for storing large amounts of crypto securely. |
| Supports Automated Systems – Can be monitored and managed using AI and real-time alerts. | Software Vulnerabilities – Bugs in wallet software or APIs can be exploited by attackers. |
| User-Friendly Experience – Quick access and withdrawals improve user satisfaction. | Requires Constant Monitoring – Needs continuous security updates, audits, and monitoring. |
Conclusion
Hot wallets are crucial for cryptocurrency platforms because they provide easy trade and rapid access to funds, but they also pose serious security threats.
Platforms integrate robust compliance and governance frameworks with multi-layered technical protections, such as multi-signature wallets, hardware security modules, real-time monitoring, and transaction restrictions, to mitigate these risks.
Crypto platforms may successfully safeguard assets while upholding user efficiency and confidence by striking a balance between strong security and user experience, as well as getting ready for next developments like MPC wallets and AI-based monitoring.
FAQ
Are hot wallets safe to use?
Hot wallets are generally safe for daily transactions if managed by a platform with strong security measures, including multi-signature wallets, hardware security modules, and real-time monitoring. However, they are more vulnerable than cold wallets because they are connected to the internet.
How do multi-signature wallets improve security?
Multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets require multiple approvals from authorized personnel before a transaction can occur. This prevents a single compromised key from being used to steal funds and reduces the risk of insider threats.
What role does monitoring play in hot wallet security?
Platforms use real-time monitoring and AI-based anomaly detection to track wallet activity. Suspicious transactions or unusual behavior trigger instant alerts, allowing the platform to respond before funds are stolen.
Can users contribute to hot wallet security?
Yes. Users should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), avoid phishing links, use strong passwords, and only interact with trusted platform apps or websites. User vigilance complements platform security.